Node Attributes: Restraint
Description
Assigns translational and rotational restraints to selected nodes.
Nodes have six degrees of freedom: three translational and three rotational. Each degree of freedom corresponds to one of the axes of the selected coordinate system. Three basic types of restraints can be applied: free, enforced or fixed; a fixed restrained is a restraint enforced with a value of zero.
Restraint attributes are freedom case dependent.
Dialog
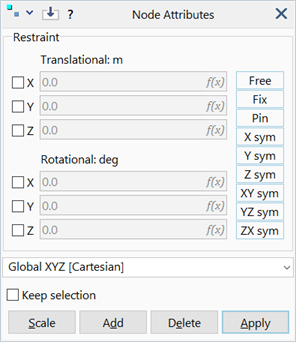
Translational / Rotational X / Y / Z
Three translational and three rotational degrees of freedom.
- If a component is not active, the corresponding degree of freedom is free.
- If a component is active, the degree of freedom is enforced with the specified value. An enforced displacement of zero fixes that degree of freedom.
Restraint Shortcuts
-
Free
Clears all prescribed displacements/rotations and sets all degrees of freedoms to be free.
-
Fix
Fixes all degrees of freedom.
-
Pin
Fixes only the translational degrees of freedom.
-
X / Y / Z Sym
Automatically restrains degrees of freedom for symmetry conditions common in 2D analyses, where the symmetry is along an axis.
-
XY / YZ / ZX Sym
Automatically restrains degrees of freedom for symmetry conditions common in 3D analyses, where the symmetry is on a plane.
Coordinate System
The coordinate system (UCS) in which the restraints are defined.
The restraint attribute remains associated with the UCS in which it is defined. Subsequent changes to the UCS will change the resulting restraint directions.
Common Controls
Units
Translational enforced restraints are in the length units of the model (e.g., m, in).
Rotational enforced restraints are in degrees.
See Also