Vertex Attributes: Translational Mass
Description
Assigns point translational mass to selected vertices.
When the geometry is meshed, the node created at the vertex will inherit the translational mass attribute (see Node Attributes: Translational Mass).
Vertex translational mass attributes are not interpolated along edges during meshing.
Translational mass attributes are independent of load and freedom cases.
Dialog
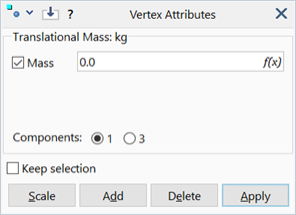
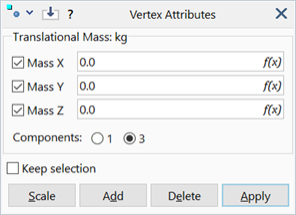
Mass (X/Y/Z)
One or three components of translational mass.
Mass Components
The translational mass components refer to the global coordinate system. There are two options:
-
1 Component
All components are the same (most common case). In this case only a single value of mass is required.
-
3 Components
The three components may be entered separately. These refer to the global Cartesian directions.
Common Controls
Units
Mass (e.g., kg, tonne, lb).
Common Uses
The most common use of the point translational mass attribute is to include the inertia and self weight of non structural items of mass in a model.
For dynamic problems, it is sometimes useful to eliminate mass in certain directions. For example, consider the dynamic analysis of a bridge containing moving vehicles. The mass of the vehicles will influence vertical and lateral vibration modes, but may not influence longitudinal modes since the vehicles are free to slide in the longitudinal direction.
See Also