SOLVERS Home: Initial Conditions (Transient Dynamic)
Description
Three options are available to define the initial conditions for the Linear and Nonlinear Transient Dynamic solvers:
- From File;
- Uniform Velocity and Acceleration; and
- Applied Nodal Velocity with Zero Acceleration.
From File
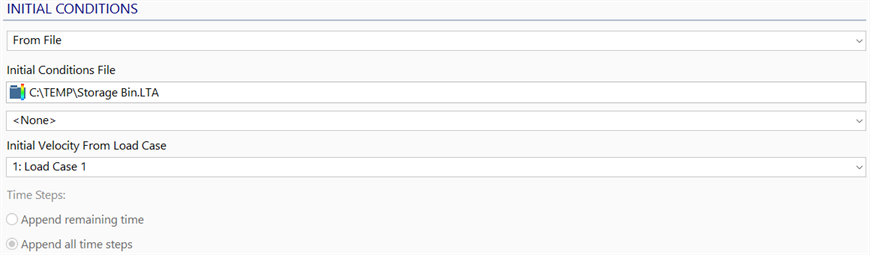
Initial Conditions File
Selects a previously generated results file (the initial file) to be used as the initial conditions for the transient dynamic analysis. Any result case from the initial file can be used as the initial case.
There are a number of uses for this feature, including the following:
- To extend a previous transient dynamic analysis by appending new result cases to the same result file.
This requires that the name of the result file specified in SOLVERS: Files be the same as the name of the initial file. If the result case used as the initial case is the last one in the initial file, the additional result cases are appended to the initial file. If the result case used as the initial case is not the last case in the initial file, all result cases after the initial case will be deleted and the new additional result cases will follow the initial case in the initial file. - To extend a previous transient dynamic analysis by saving the new result cases to a new result file.
This is similar to the previous use except that the new result cases are not appended to the initial file but saved to a new file. This requires that the name of the new result file specified in SOLVERS: Files be different from the name of the initial file. The new result cases are saved to the specified result file overwriting that file (there is no option to append to that file when it is a different name from the initial file). - To start a transient dynamic analysis using a static analysis as the initial conditions.
Examples of this include using a nonlinear static analysis result case as the initial conditions for a nonlinear transient dynamic analysis, using a quasi-static analysis as the initial conditions for a nonlinear transient dynamic analysis and using a linear static analysis as the initial conditions for a linear transient dynamic analysis. In all of these, the results are stored in the file specified in SOLVERS: Files, overwriting that file in each case.
Include Stress Stiffening
If set, the geometric stress stiffness matrix, [KG], is added to the structural stiffness matrix, otherwise only the structural stiffness matrix is assembled.
This option will only be available when a linear transient dynamic analysis using the Full System solution option includes a linear static results file for the initial conditions. For the Mode Superposition solution option, the analysis uses the same stiffness matrix as used in the natural frequency analysis, with or without the geometric stress stiffness matrix.
Initial Velocity From Load Case
Selects a load case with nodal initial velocity attributes to be used in the transient dynamic analysis as the velocity at time zero. This option offers the flexibility of defining a non-uniform initial velocity distribution.
This option will be available in the Linear Transient Dynamic solver when the initial conditions file is a linear static result file, and in the Nonlinear Transient Dynamic solver when the initial conditions file is either a nonlinear static or a quasi-static result file. When the initial files are transient dynamic files, the option is not relevant because the velocity will already be contained within those initial files.
Time Steps
This option is applicable only when a time-based solution is used as the initial condition file.
-
Append remaining time
Time steps defined in the time table (SOLVERS: Time Steps) that represent a time earlier than the time instance of the result case used as the initial case are skipped. Time steps that represent a time after the time instance of the initial case are added. For example, if the initial case represents time=25 s, and the table defines 50 steps of 1 s, at the completion of the analysis the result file will contain result cases up to and including time=50 s. In the case where the maximum time in the time table represents a time less than or equal to the time instance of the initial case, no further result steps will be produced.
-
Append all time steps
Time steps defined in the time table (SOLVERS: Time Steps) are added to the time instance of the result case used as the initial case. For example, if the initial case represents time=25 s, and the table defines 50 steps of 1 s, at the completion of the analysis the result file will contain result cases up to and including time=75 s.
Uniform Velocity and Acceleration
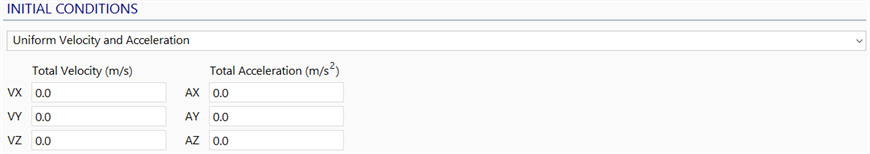
Initial Velocity
The velocity in the global XYZ axes at time zero.
The same initial velocity is applied to all unrestrained degrees of freedom in the model.
Initial Acceleration
The acceleration in the global XYZ axes at time zero.
The same initial acceleration is applied to all unrestrained degrees of freedom in the model.
Applied Nodal Velocity with Zero Acceleration
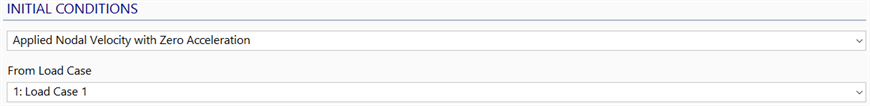
From Load Case
Selects a load case with nodal initial velocity attributes to be used in the transient dynamic analysis as the velocity at time zero.
This option offers the flexibility of defining a non-uniform initial velocity.
Acceleration is taken as zero at time zero.
See Also