Creep: Concrete Creep and Shrinkage - User-Defined
Description
Defines concrete creep behaviour via selected Strain vs Time tables.
Toolbar Functions
See LAYOUTS: Creep.
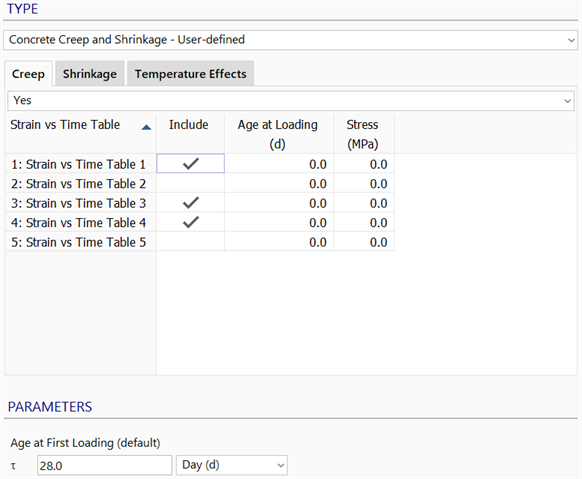
Creep Tab
Strain vs Time tables can be defined in LAYOUTS: Tables and selected here to represent material creep behaviour. Each table is associated with a stress level and an Age at Loading. The table then represents the creep strain accumulated over time when the material is subjected to the specified stress level and age at loading.
The creep strain data entered is curve fitted by the solver to a Concrete Creep: Generalised Kelvin Chain (Creep function) according to parameters set under SOLVERS Parameters: Creep.
Include
If set, the Strain vs Time table contributes to the material creep behaviour.
If not set, the corresponding row of data is ignored.
Age at Loading
The age of concrete at the time of first loading, when the Strain vs Time table was measured.
Stress
The stress level applied to the concrete, when the Strain vs Time table was measured.
Age at First Loading (default)
Specifies the age of the concrete at the beginning of the analysis.
Note that the effective age at first loading can also be dependent on the Cement Curing Age of Loading parameters defined in the Temperature Effects Tab.
Specific Creep
A frequently used measure of concrete creep obtained from uniaxial testing is the specific creep which is defined as:
where
is time;
is the age of concrete at first loading;
is the creep strain; and
is the applied stress in the uniaxial test.
Therefore, as the creep strain is considered to be proportional to the loading
, the specific creep
can be considered to be the creep strain at time
produced by a sustained unit stress first applied at
.
The relationship between the creep coefficient and specific creep is given below:
Shrinkage Tab
The Shrinkage tab specifies the concrete shrinkage properties.
See Creep: Concrete Creep and Shrinkage - Shrinkage.
Temperature Effects Tab
The Temperature Effects tab specifies properties that account for temperature effects on the creep and shrinkage of concrete.
See Creep: Concrete Creep and Shrinkage - Temperature Effects.
See Also