Creep: Secondary Power Law Creep
Description
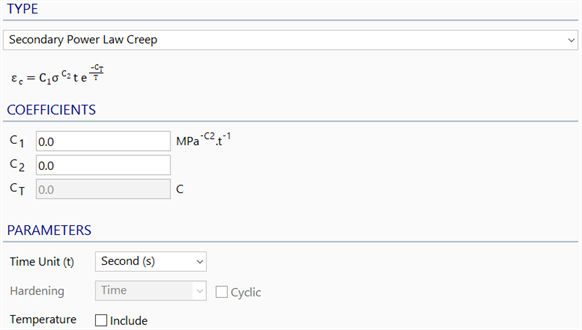
Defines creep data parameters according to the secondary power creep law.
This simple secondary power law relationship has been found to provide an excellent description of steady state creep for many materials, and is therefore the most commonly used uniaxial creep law.
Toolbar Functions
See LAYOUTS: Creep.
COEFFICIENTS
C1 is the creep strain coefficient.
C2 is the creep stress index.
CT is the creep temperature coefficient.
PARAMETERS
Time Unit (t)
The unit of time in which the coefficients are specified.
Hardening
Not applicable to this creep law.
Temperature
This option sets whether the creep law is dependent on temperature or not.
If set, the CT parameter may be specified and the accumulation of creep strain is influenced by the nodal temperatures. The Property Temperature Dependence (see SOLVERS Home: Case Dependence tab) also needs to be assigned in the Quasi-static or Nonlinear Transient Dynamic solver to consider the creep temperature dependence.
If not set, the CT parameter(s) is not used and the creep behaviour is independent of any applied nodal temperatures.
See Also