Node Attributes: Temperature
Description
Assigns the temperature value and its type to selected nodes.
For the time dependent solvers, the attribute can reference a Temperature vs Time table to define a temperature that varies with time (see Special Topics: Table Types).
In the structural solvers, the effect of temperature at a node is to generate a thermal expansion in the elements connected to the node.
In the heat solvers, a set node temperature is analogous to a prescribed nodal displacement in the structural solvers (see Node Attributes: Restraint).
Temperature attributes are load case dependent.
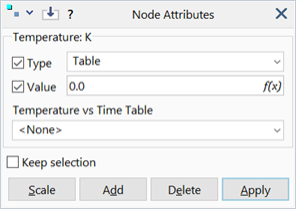
Dialog
-
Reference
Sets the nodal temperature as the reference temperature in the load case.
By default, all nodes are initially at the reference temperature. In heat transfer analysis the temperature at nodes with this temperature type is allowed to change. In the structural solvers, when all the nodes in an element are at the reference temperature, zero thermal strain is produced.
-
Fixed
Sets the nodal temperature to a fixed value.
In heat transfer analysis the temperature remains fixed at the specified value throughout the solution. In the structural solvers, nodes with this setting generate thermal strains calculated from the difference between the fixed temperature and the reference temperature in the load case.
-
Initial
Sets the nodal temperature as an initial temperature. This is applicable only to the Transient Heat Solver.
The assigned temperature is applied as an initial condition (i.e., at the start of the first time step). The temperature at the node then changes for subsequent time steps. For all other solvers the value is treated as a Fixed value.
-
Table
Set the nodal temperature to vary as a function of time defined using a Temperature vs Time Table. This is applicable only to the Transient Heat, Transient Dynamic and Quasi-static solvers.
During a time-dependent analysis, the value of temperature at a node is determined by interpolating it from the table based on the current solver time. For all other solvers the Factor vs Time Table is ignored.
Value
Scalar value of temperature.
Temperature vs Time Table
The table that defines the temperature as a function of time. Available when type is set to Table.
If set, the temperature specified under Value is superseded by the values defined in the Temperature vs Time table.
This is applicable only to the Transient Dynamic solver, Transient Heat and Quasi-static solvers.
See Special Topics: How Solvers Use Tables.
Common Controls
Units
Absolute scale (K or R) or relative scale (°C or °F).
In applications where the solution is a linear function of temperature or a function of temperatures difference (i.e., T-Tref), either scale can be used. Examples include structural thermal expansion problems and heat transfer problems that involve only conduction and convection. The relative scale is normally preferred in these cases as the results are easier to interpret. For problems involving radiation the absolute temperature scale should be used. If the model uses a relative scale, Straus7 automatically converts to an absolute scale for the solution, but the results are given in the user's chosen scale.
See Also