Insert Multi-element: Load Patch Plates on Beam Polygons
Description
Inserts load patch plate elements over frameworks of polygons formed by selected beam elements.
The frameworks may consists of any number of polygon segments in either 2D or 3D.
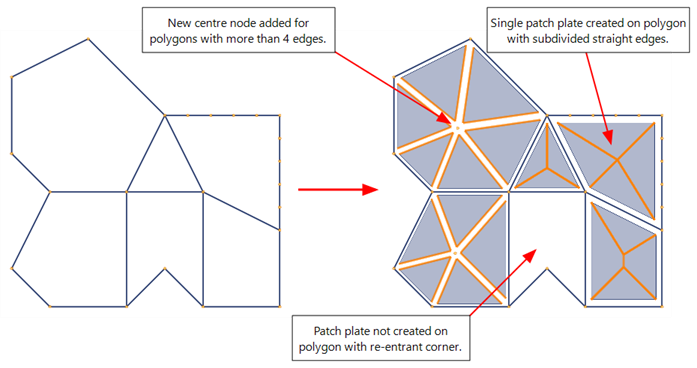
Where possible, single triangular and quadrilateral patch plates are placed over polygons with three and four sides respectively, even if a straight edge of a polygon consists of more than one beam element.
Where it is not possible to insert single patch plates over a polygon, multiple triangular patch plates are connected to a new node located at the average position of the nodes on the polygon.
Patch plates are not created on polygons with re-entrant corners.
Dialog
Polygons with 5 or more edges
The default tributary area partitioning of loads on a quadrilateral does not generally apply when the polygon has five or more edges, therefore two options are offered to deal with this case.
-
Triangular load
Applies a triangular load distribution to beam polygons with five or more edges.
-
Constant load
Applies a constant load distribution for beam polygons of five or more edges.
Group
-
Beam group
If set, inserted load patch plates are added to the source beam element group.
-
Specified group
If set, inserted load patch plates are added to the specified group. See Target group.
Plane Tol
An angular tolerance.
For any closed polygon with four edges or more (with no re-entrant corners) each consecutive set of three edges is treated as a triangle. The normal of each triangle is compared with the normal of the adjacent triangle (formed with the adjacent set of three edges). If the angle between the normals of these triangles is within the specified angular tolerance, the closed polygon is considered to be planar, and patch plates are created. If the angle between the normals of the triangles is greater than the angular tolerance, load patches are not created on that polygon.
See warped plates for an example of a non-planar polygon (Entities: Plate Elements).
Keep Selection
If set, entities remain selected after executing the function. Additional functions may then be applied without the need to reselect the entities. If not set, selected entities will be unselected after the function is executed.
See Also